CH:3 Life Processes in living Organisms Part -2 Solutions Class 10th | Life Processes in living Organisms SSC Class 10 Questions And Answers
Complete the following chart:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
|---|---|
| Reproduction that occurs with the help of somatic cells is called asexual reproduction. | Reproduction that occurs with the help of gametes is called sexual reproduction. |
| Single parent is sufficient for asexual reproduction. | Male and female parent are necessary for sexual reproduction. |
| This reproduction occurs with the help of mitosis only. | This reproduction occurs with the help of both mitosis and meiosis. |
| New individual formed by this method is genetically identical to the parent (clone). | New individual formed by this method is genetically different from parents. |
| Asexual reproduction occurs in different individuals by various methods like binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation, spore production, etc. | Sexual reproduction occurs through fertilization, leading to the formation of a zygote which develops into a new organism. |
Fill in the blank:
In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ ----------------.
Solution:
In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ testes.
Fill in the blank:
In humans, ------ chromosome is responsible for maleness.
Solution:
In humans, the Y chromosome is responsible for maleness.
Fill in the blank:
In the male and female reproductive system of humans, the ______ gland is the same.
Solution:
In the male and female reproductive system of humans, the gonads gland is the same.
Fill in the blank:
Implantation of the embryo occurs in ------.
Solution:
Implantation of the embryo occurs in the uterus.
Fill in the blank:
---------- type of reproduction occurs without the fusion of gametes.
Solution:
Asexual type of reproduction occurs without the fusion of gametes.
Multiple Choice Question:
Body breaks up into several fragments and each fragment starts to live as a new individual. This is ______ type of reproduction.
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Regeneration
- Binary fission
Solution:
The correct answer is Fragmentation.
Fill in the blank:
Pollen grains are formed by ______ division in locules of anthers.
Solution:
Pollen grains are formed by meiotic division in locules of anthers.
Complete the paragraph with the help of words given in the bracket:
(Luteinizing hormone, endometrium of uterus, follicle stimulating hormone, estrogen, progesterone, corpus luteum)
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of ____________. This follicle secretes estrogen. ____________ grows/regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of ____________, fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and ____________ is formed from remaining part of follicle. It secretes ____________ and ____________. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of ____________ are activated and it becomes ready for implantation.
Solution:
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). This follicle secretes estrogen. Endometrium of uterus grows/regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of Luteinizing Hormone (LH), fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and Corpus Luteum is formed from the remaining part of the follicle. It secretes Estrogen and Progesterone. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of Endometrium of Uterus are activated, and it becomes ready for implantation.
Explain with examples types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms.
Solution 1: Scientific and Written Exam Answer
Asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms occurs through various methods, where a single parent cell divides to form new individuals without gamete fusion. The main types include:
- Binary Fission: The parent cell splits into two identical daughter cells. Example: Amoeba, Paramecium.
- Multiple Fission: The nucleus divides multiple times, forming many daughter cells. Example: Plasmodium.
- Budding: A small outgrowth (bud) develops on the parent cell and detaches as a new organism. Example: Yeast.
- Fragmentation: The organism breaks into smaller fragments, each developing into a new organism. Example: Oscillatoria (cyanobacteria).
These methods allow unicellular organisms to reproduce rapidly and survive in various environments.
Solution 2: Simple and Understandable Answer
Unicellular organisms reproduce asexually, meaning they don't need a partner. They simply split or grow new parts to make more of themselves.
- Binary Fission: One cell divides into two. Example: Amoeba.
- Multiple Fission: One cell makes many tiny cells at once. Example: Plasmodium (causes malaria).
- Budding: A small part of the cell grows, breaks off, and becomes a new organism. Example: Yeast.
- Fragmentation: The cell breaks into pieces, and each piece grows into a new one. Example: Oscillatoria.
These methods help tiny organisms multiply quickly!
Explain the concept of IVF.
Solution 1: Scientific and Written Exam Answer
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is an advanced reproductive technology used to help individuals conceive. The process involves:
- Eggs are extracted from a female’s ovaries.
- The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory (outside the body).
- The fertilized egg (zygote) develops into an embryo.
- The embryo is implanted into the uterus for further development.
IVF is commonly used to treat infertility due to blocked fallopian tubes, low sperm count, or other reproductive issues.
Solution 2: Simple and Understandable Answer
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) is a method to help couples have a baby when natural pregnancy is difficult. Doctors take a woman's egg and mix it with a man's sperm in a lab. When a baby embryo forms, it is placed in the mother’s womb to grow.
IVF is useful when couples face problems like blocked tubes or weak sperm. It gives hope to families who want children.
Which precautions will you follow to maintain reproductive health?
Solution 1: Scientific and Written Exam Answer
Reproductive health is essential for overall well-being. To maintain it, the following precautions should be taken:
- Maintain Personal Hygiene: Regular washing of genital areas helps prevent infections.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins supports reproductive health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves hormonal balance and overall health.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Early detection of reproductive health issues ensures proper treatment.
- Avoid Addictions: Smoking, alcohol, and drugs negatively affect reproductive organs.
By following these measures, individuals can ensure a healthy reproductive system and prevent diseases.
Solution 2: Simple and Understandable Answer
To stay healthy and protect your reproductive system, follow these simple steps:
- Keep Clean: Wash private parts daily to avoid infections.
- Eat Healthy: Eat fruits, vegetables, and proteins to stay strong.
- Exercise Regularly: Keep your body fit and active.
- Visit a Doctor: Regular checkups help catch problems early.
- Avoid Bad Habits: Smoking and alcohol harm the reproductive system.
These habits will help you stay healthy and avoid future health problems!
What is menstrual cycle? Describe it in brief.
Solution 1: Scientific and Written Exam Answer
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in the female reproductive system that prepares the body for pregnancy. It lasts for about 28 days on average and consists of four main phases:
- Menstrual Phase (1-5 Days): The endometrium (inner lining of the uterus) sheds, causing bleeding.
- Follicular Phase (6-13 Days): The follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, which release estrogen.
- Ovulation Phase (14th Day): A mature egg is released from the ovary due to a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Luteal Phase (15-28 Days): The ruptured follicle forms the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to maintain the uterine lining for possible pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the cycle restarts.
The menstrual cycle plays a crucial role in female reproduction and is controlled by various hormones.
Solution 2: Simple and Understandable Answer
The menstrual cycle is a natural process in females that happens every month. It prepares the body for pregnancy. It has four main stages:
- Menstrual Phase: Bleeding happens as the uterus removes its old lining.
- Follicular Phase: A new egg starts growing inside the ovary.
- Ovulation: The egg is released from the ovary, ready for fertilization.
- Luteal Phase: The body prepares for pregnancy. If no fertilization happens, the cycle starts again.
The entire cycle lasts about 28 days. If a woman gets pregnant, her cycle stops until after childbirth.
In case of sexual reproduction, newborns show similarities in characteristics. Explain this statement with suitable examples.
Solution 1: Scientific and Written Exam Answer
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, which results in the inheritance of genetic material from both parents. This process ensures that offspring exhibit similarities with their parents in terms of physical traits and genetic characteristics.
The inheritance of traits follows the principles of genetics as proposed by Gregor Mendel. The DNA of the offspring is a combination of genetic material from both parents, leading to similarities in characteristics.
Example: If a child inherits genes for eye color from both parents, the child's eye color will resemble either the mother’s or the father’s eye color. Similarly, other features such as hair texture, height, and skin tone are also inherited due to genetic transmission.
Although the offspring share similarities with their parents, they are not identical due to the recombination of genetic material during gamete formation.
Solution 2: Simple and Understandable Answer
In sexual reproduction, a baby receives traits from both parents because it is formed by the combination of sperm (from the father) and egg (from the mother). This is why children often look similar to their parents.
Example: If a father has curly hair and the mother has straight hair, the child may have wavy hair, which is a mix of both.
Other characteristics such as skin color, height, and facial structure are also inherited, but every child is unique because the genetic combination is different in each case.
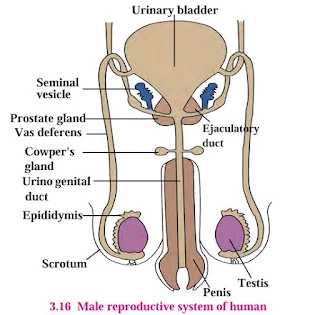
Sketch the labeled diagram: Human male reproductive system
Solution:
Below is the labeled diagram of the human male reproductive system:
This diagram illustrates the key components of the male reproductive system, including the testis, scrotum, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate gland, Cowper's gland, urethra, and penis.
The male reproductive system is responsible for sperm production and delivery. The testes produce sperm and testosterone, which are essential for reproduction. The seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper’s gland secrete fluids that nourish and transport sperm.
Key Components:
- Testis: Produces sperm and male hormones.
- Scrotum: Holds and protects the testes.
- Epididymis: Stores and matures sperm.
- Vas Deferens: Transports sperm from epididymis.
- Seminal Vesicle: Produces seminal fluid for sperm nourishment.
- Prostate Gland: Secretes fluid that helps sperm motility.
- Cowper's Gland: Produces mucus-like fluid for lubrication.
- Urethra: Passageway for urine and semen.
- Penis: Organ for sperm delivery.
Importance: The male reproductive system plays a crucial role in human reproduction by producing and delivering sperm cells essential for fertilization.
Sketch the labeled diagram: Human female reproductive system
Solution:
Below is the labeled diagram of the human female reproductive system:
The human female reproductive system consists of several essential organs responsible for egg production, fertilization, and pregnancy.
Key Components:
- Ovary: Produces eggs (ova) and female hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- Oviduct (Fallopian Tube): Transports eggs from the ovary to the uterus and is the site of fertilization.
- Uterus: A muscular organ where the fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus.
- Vagina: The birth canal that connects the external genitalia to the uterus.
Importance: The female reproductive system plays a crucial role in reproduction, supporting conception, pregnancy, and childbirth.
Sketch the labeled diagram: Flower with its sexual reproductive organs
Solution:
Below is the labeled diagram of a flower showing its sexual reproductive organs:
Flowers contain reproductive structures responsible for the production of seeds and the continuation of plant species.
Key Components:
- Gynoecium (Carpel): The female reproductive part consisting of stigma, style, and ovary.
- Androecium: The male reproductive part consisting of anthers and filaments.
- Stigma: The top part of the carpel where pollen lands for fertilization.
- Ovary: Contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization.
- Anther: Produces pollen grains containing male gametes.
- Filament: Supports the anther.
- Corolla (Petals): Attracts pollinators with its bright colors.
- Calyx (Sepals): Protects the flower bud before it blooms.
- Pedicel: The stalk that supports the flower.
Importance: Flowers play a crucial role in plant reproduction, ensuring genetic diversity and seed formation.
Sketch the labeled diagram: Menstrual Cycle
Solution:
Below is the labeled diagram of the menstrual cycle:
The menstrual cycle is a natural biological process in females that prepares the body for pregnancy. It typically lasts 28 days and consists of different phases.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle:
- Menstrual Phase (Day 1-5): The shedding of the uterine lining occurs, leading to menstruation.
- Follicular Phase (Day 6-13): The endometrial lining regenerates, and follicles develop due to the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estrogen.
- Ovulation (Day 14): A mature egg is released from the ovary due to a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Luteal Phase (Day 15-28): The corpus luteum forms, secreting progesterone and estrogen, which prepare the uterus for implantation.
Key Hormones Involved:
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) stimulates follicle growth.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) triggers ovulation.
- Estrogen helps in the regeneration of the endometrial lining.
- Progesterone maintains the endometrial lining for potential pregnancy.
Importance: The menstrual cycle is essential for reproductive health, regulating fertility and ensuring hormonal balance.
Give the name: Hormones related to the male reproductive system.
Solution:
- Testosterone
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Name two hormones secreted by the ovary of the female reproductive system.
Solution:
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
Name the two types of twins.
Solution:
- Identical (Monozygotic) Twins
- Fraternal (Dizygotic) Twins
Give the names: Any two sexual diseases.
Solution:
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
Give the name: Methods of family planning.
Solution:
- Barrier Methods (e.g., Condoms)
- Oral Contraceptive Pills
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
- Sterilization (Vasectomy, Tubectomy)
- Natural Methods (e.g., Rhythm Method)
Gender of the child is determined by the male partner of the couple. Explain with reasons whether this statement is true or false.
Solution:
This statement is true.
Reason:
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, including one pair of sex chromosomes (XX in females and XY in males).
- The egg from the female always carries an X chromosome.
- The sperm from the male may carry either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome.
- If the sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child will be female (XX).
- If the sperm carrying a Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child will be male (XY).
- Since the male provides either an X or a Y chromosome, the gender of the child is determined by the male partner.
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
Solution:
Asexual reproduction in plants is a mode of reproduction in which offspring are produced without the involvement of seeds or gametes. It results in genetically identical offspring (clones) of the parent plant.
Types of Asexual Reproduction:
- Vegetative Propagation: New plants grow from roots, stems, or leaves. Examples:
- Stem: Sugarcane, Potato (tuber), Ginger (rhizome)
- Root: Sweet potato
- Leaf: Bryophyllum (new plants develop from leaf margins)
- Budding: A small bud grows on the parent plant and detaches to form a new individual. Example: Yeast.
- Fragmentation: The parent body breaks into fragments, and each fragment develops into a new plant. Example: Algae (Spirogyra).
- Spore Formation: Plants produce spores that germinate into new plants under suitable conditions. Example: Fungi, Mosses, Ferns.
Asexual reproduction allows rapid multiplication of plants and is widely used in horticulture and agriculture.
Modern techniques like surrogate mother, sperm bank, and IVF technique will help human beings. Justify this statement.
Solution:
Modern reproductive techniques have greatly helped individuals and couples facing fertility issues. These techniques provide alternative methods for conceiving and carrying a child.
Justification:
- Surrogate Mother: A woman carries and delivers a baby for another couple or individual. It helps those unable to carry a pregnancy due to medical reasons.
- Sperm Bank: Sperm from healthy donors is preserved and used for artificial insemination, benefiting couples with male infertility or single women wanting children.
- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization): The fertilization of an egg and sperm occurs outside the body in a lab. The resulting embryo is implanted into the uterus, helping couples with infertility issues.
These techniques have revolutionized reproductive medicine, providing hope to many families struggling with infertility.
Explain sexual reproduction in plants.
Solution:
Sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of male and female gametes, leading to the formation of seeds and offspring with genetic variation.
Process of Sexual Reproduction in Plants:
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) of a flower. It can be of two types:
- Self-Pollination: Pollen from the same flower fertilizes the ovule.
- Cross-Pollination: Pollen from one flower fertilizes another flower of the same species.
- Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gametes in the ovary forms a zygote.
- Seed and Fruit Formation: The zygote develops into an embryo, and the ovary transforms into a fruit.
- Seed Germination: Under suitable conditions, the seed grows into a new plant.
Sexual reproduction ensures genetic diversity, helping plants adapt to environmental changes and evolve over time.
One of the following does not reproduce by spore formation method. This is:
(a) Rhizopus fungus
(b) Penicillium fungus
(c) Yeast fungus
(d) Mucor fungus
Solution:
The correct answer is (c) Yeast fungus.
Explanation: Yeast reproduces primarily by budding, not by spore formation. In budding, a small outgrowth (bud) forms on the parent cell, gradually enlarges, and then separates to become a new yeast cell. In contrast, Rhizopus, Penicillium, and Mucor fungi reproduce by producing spores.