Tertiary Economic Activities Exercise | Class 12 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities
1. Complete the Chain
Q: 1.
| A | B | C |
| (1) Matheran | (1) Tea | (1) Communication |
| (2) GPS | (2) Atlantic Ocean | (2) Tertiary Activity |
| (3) Sri Lanka | (3) Satellite | (3) Export |
| (4) Panama Canal | (4) Tourism | (4) Pacific Ocean |
Solution:
| A | B | C |
| (1) Matheran | (1) Tourism | (1) Tertiary Activity |
| (2) GPS | (2) Satellite | (2) Communication |
| (3) Sri Lanka | (3) Tea | (3) Export |
| (4) Panama Canal | (4) Atlantic Ocean | (4) Pacific Ocean |
2. Choose the correct option.
Q: 1. Tertiary activities include
[a] Use of natural resources
[b] Finished product
[c] Raw material
[d] Transportation
Solution:
[d] Transportation
Q: 2.Natural ports
[a] Kochi
[b] JNPT
[c] Delhi International Terminal
[d] Nagpur Cargo Hub [MIHAN]
Solution:
[a] Kochi
Q: 3.Trans-Australian Railway connects
[a] Perth - Sydney
[b] Perth - Vladivostok
[c] Sydney - Vancouver
[d] Vancouver - Vladivostok
Solution:
[b] Perth - Vladivostok
3. Give geographical reasons.
Q: 1.Tertiary activities include both services and exchapge.
Solution:
- Transportation, communication, trade and commerce are the main tertiary activities.
- Road, rail and airways are the important modes of transportation, which help in exchange of goods and services. Therefore, it is a service activity.
- Transportation provides facilities for the movement of goods from areas of surplus to areas of scarcity produced in primary and secondary activities.
- Credit facilities, banking facilities, marketing are also tertiary activities, they provide services to people.
- Postal services, shopkeepers, vegetable sellers, fruit sellers, etc., are also included in service activities.
Q: 2.The proportion of airways as means of transportation is increasing.
Solution:
- Air transport is an important enabler to achieve economic growth and development.
- In the global world, there is exchange of goods between countries. Therefore, there is more use of air transport to carry perishable, valuable and light goods from surplus areas to scarcity areas.
- It facilitates integration into global economy and provides vital connectivity on a national, regional and international scale.
- Nowadays tourism is the fastest growing industry; air transport is more used for international tourism.
- Therefore, the proportion of airways as means of transportation is increasing.
Q: 3.Geographical diversity is responsible for trade to occur.
Solution:
- The geographical diversity is the set of physical, human and cultural elements differentiated from each other that converge in the relatively small geographic space that is part of the same zone, region or country.
- If you take into consideration natural regions of the world, each region is different from another.
- The natural resource available in one country will be different from the ones available in different regions.
- There is variation in climate, soil, minerals, forest, relief, water supply etc.
- Depending upon the availability of geographical factors, there is specialisation of certain economic activities in certain areas and there is trade from surplus areas to scarcity areas. For example, in one region, plenty of oil is available while in another region no oil reserves are available.
- This variation in distribution of oil will be responsible for the development of trade between oil rich and oil poor countries.
- Thus, geographical diversity is responsible for trade to occur.
4. Write short notes on.
Q: 1.Importance of satellite as means of communication.
Solution:
- A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via. transponder.
- Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet and military applications.
- The information about physical and human factors is obtained from satellite communication.
- Satellite communication is used in remote islands, in some countries and continents where landline telecommunication is rare or not available.
- As television becomes the main market, its demand for satellite communication becomes very important.
- Satellites are also used for internet communication, military communications, etc.
- Thus, importance of satellite as means of communication is increasing.
Q: 2.Role of transportation in trade.
Solution:
- Transport support trade and industry in carrying raw material to the place of production and distribution of finished products for consumption.
- Transport means to make goods available to consumers.
- Transport makes possible movement of goods from one place to another with great ease and speed.
- Trade means exchange of goods and services. In trade there is movement of goods from surplus areas to scarcity areas. The movement of goods is possible only because of transport.
- In other words, without the help of transport development of trade is not possible.
- Thus, transport plays an important role in economic development and globalisation of trade.
Q: 3.Tourism and GDP.
Solution:
- Tourism is vital for the success of many economies around the world.
- Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs and develops the infrastructures of the country.
- It also creates jobs in agriculture, communication, health and educational sectors.
- The government that depends on tourism, invests a lot in the infrastructure of the country. They construct new roads and highways, develop parks, improve public places, and set up airports, etc.
- With augmenting facilities, more and more tourists are attracted in such countries, thus, there is boosting of the GDP.
5. Differentiate between.
Q: 1.Secondary Economic Activities and Tertiary Economic Activities
Solution:
| Secondary Economic Activities | Tertiary Economic Activities |
| (i) Secondary activities are concerned with activities adding value to already existing products from primary activities. | (i) Tertiary activities are concerned with providing services rather than providing material goods. |
| (ii) Development of secondary activities depends upon the production of resources in primary activities. | (ii) Development of tertiary activities depends upon the development of secondary activities. |
| (iii) Manufacturing and construction are important secondary activities. | (iii) Trade, transport communication, banking, insurance, etc., are tertiary activities. |
| (iv) Secondary activities produce goods and commodities. | (iv) Tertiary activities help reach these goods and commodities to the consumers. |
| (v) Secondary activities may be away from the market and settlement. | (v) Tertiary activities are always near the market and settlement. |
Q: 2.Quaternary Activities and Quinary Activities
Solution:
| Quaternary Activities | Quinary Activities |
| (i) Quaternary activities refer to those activities where the task is to think, research and develop ideas. | (i) Quinary activities involve work related to administration. |
| (ii) Confined to research, training and education. | (ii) Confined to the highest-level decision taking and policy making. |
| (iii) Software developers, statisticians, hospital staff, teachers, financial planners tax consultants, people working in theatres, etc., comes under quaternary activities. | (iii) Senior business executives, government officials, scientists, judges, etc., comes under quinary activities. |
Q: 3.Waterways and Airways
Solution:
| Waterways | Airways |
| (i) Development of water transport needs courted area with broken coastlines. | (i) Development of airways needs favourable climate, advance technology and plain land for airports. |
| (ii) This is the cheapest mode of transport. | (ii) This is an expensive mode of transport. |
| (iii) Heavy and bulky goods are transported, e.g., minerals, oil, coal, machinery, etc. | (iii) Light, perishable and expensive goods are transported, e.g., electronic goods, gold, silver, fish, dairy products, etc. |
| (iv) Slow mode of transportation. | (iv) Fast mode of transportation. |
| (v) More used for goods transport than passengers’ transport | (v) More used for passengers’ transport than for goods transport. |
6. Answer in Detail
Q: 1.Explain the factors affecting trade between two countries.
Solution:
Trade refers to transfer of goods or services from one person to another or from one country to another. Factors which affect the trade are natural resources, climate, population, culture, economic cost, specialization, etc.
Natural resources : Distribution of natural resources is uneven. The natural resources available in one country differs from another. Because of this uneven distribution of resource, there is trade between resources surplus and resource deficit.
Climate : Climate mainly affects the plants and animals in a region. In the areas of different climate, there are different types of plants and animals. Example, in the tropical countries like Sri Lanka whose major export is tea or Malaysia and Indonesia, whose major export is rubber. This occurs naturally because of favourable climate for growing tea and rubber plants in these countries.
Population : Population size, distribution and density are different in different countries. This leads to difference in production and consumption and hence trade occurs.
Standard of living can also determine the demand for various goods and services. The country with less population depends more on trade because fewer human resources is engaged in production of goods.
Culture : Some countries are known for their specific art and craft, based on their culture, specific production of goods which have worldwide market, for e.g., Kashmiri shawls or Iranian carpets.
Economic Cost : Cost of production is the major factor in the process of production. It is cheaper to import certain goods than producing it in the country itself. For example, it is cheaper to import tea from India and Sri Lanka than producing it in England.
Specialisation : Due extremely favourable factors of production, some countries have specialisation for certain goods and they have name and fame in the world market, so they develop export trade. For example, watches of Switzerland or electronic goods of Japan or tender beef of Argentina.
Government Policy: Government policy about export or import affects trade. For example, Government may increase import duties of some goods, to encourage people to buy domestic goods. Thus, import trade of those goods goes down.
Q: 2.Development of transportation is dependent on geographical factors. Explain.
Solution:
- Various geographical factors affect the development of transport.
- Relief, climate and location are the three most important factors that affect the development of transportation.
- It is easier to build roadways and railways in plain areas.
- Dense forests, hilly and mountainous regions affect the construction of roads and railways, in Africa and South America.
- Coastal location with broken coast lines is favourable for development of ports and harbours.
- For the development of airways; favourable climate and plain region for construction of airports are essential.
- Foggy and smoggy weather and high peaks will be obstacles for the development of air transport.
Q: 3.Why is transportation system important in the development of any nation?
Solution:
- Transportation plays important role in rapid economic growth of a nation.
- The introduction of railways has been historically the most important and powerful single factor in the process of economic development of industrial nations of the world like USA, France, Germany, Japan, etc.
- The significance of transportation in economic activity is found in its effects on both human wants and satisfaction of wants through production and distribution of goods.
- Transportation increases the quality and variety of consumer goods, thereby stimulating the demand and development of trade and economy of the nation.
- Transport provides various employment opportunities and boosts up the economy of the country. For example, many people got employment in construction work of Metro rail track.
Q: 4.Tertiary activities are expanding day-by-day. Explain the statement.
Solution:
- Tertiary activities act as the link between primary and secondary activities.
- These activities are mostly in the form of services.
- Tertiary activities include transport and communication, trade, loading and unloading of goods, banking, insurance, marketing, export, etc.
- Providing public services like hospital, education, research and development, administration, etc., are also included in tertiary activities.
- With increasing industrialisation population growth and trade, number of people working in banking, insurance, tax consultants, software developers, teachers, etc., went on expanding day by day.
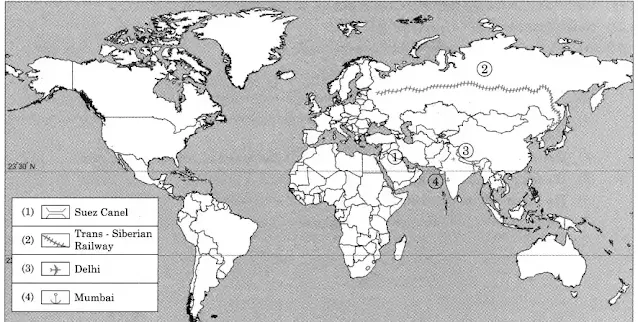
7. On an outline map of the world, show the following with the help of suitable index
[1] A canal bringing radical changes in sea transport.
[2] Railway connecting two continents.
[3] An international airport in India.
[4] An important port in India.
Solution:
8. Read the given passage and answer the following Q:s
Careful planning and implementation is necessary for economic development of any country. In the tourism sector the need for planned development is of great importance. It involves many industries working together in a complex way and needs special attention. Planning basically tries to allot limited resources between various competitors with a view to maximize output, income and employment and to make sure different sectors have fair growth.
Tourism planning is a process through which the set goals can be achieved and the various choices linked to tourism development can be addressed. It is a long term and constant process of preparing, upgrading and improving a destination for tourist.
Communities are the basic elements of tourism. It mainly depends upon the level of acceptance shown by local communities. In the process of planning their involvement is essential. The development of tourism creates impact on mainly environment, socio-culture and economy of the host community at any destination. These impacts produce both negative as well as positive impacts. Planning is necessary to reduce the negative impact and boost the positive impact for sustainable development of a destination.
Tertiary Economic Activities Exercise | Class 12 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities
Geographical explanation
While reading the passage, you would
have come across many human occupations.
These are the economic activities carried out
by humans. Out of them, some of the activities
are completely dependent on nature. We obtain
natural resources out of such activities. These
activities are primary activities.
Man cannot use some of the products
received from these activities directly. These
products can be used again by increasing their
values or making them more durable.
In that
case, these products are processed. This creates
new and different products. These are usable,
more durable and can be sold at higher prices.
Through processing, these activities become a
part of secondary activities. Secondary activities
are mainly dependent on products obtained from
primary activities.
There are activities which act as the link
between the primary and secondary activities
and are complementary to both of them. These
are mostly in the form of services.
If you want
a particular service you will have to pay for
it. These include buying and selling of goods, means of transportation and communication,
loading and unloading of goods, credit facilities,
marketing, import and export, etc. Providing
public services are also a part of it. Other services
like knife grinders, vegetable sellers, shopkeepers,
passenger’s carriers, postal services, etc. are also
included in tertiary activities. All these services
are called tertiary economic activities. (Fig.6.1)
In tertiary occupations, there is no derivation
from the nature as it is in primary activities.
There may be some products manufactured like
secondary activities but they are in the form of
services offered. As these activities are mainly
of the service category, these occupations are
also known as the ‘service sector’.
The distribution of many of these services
is dependent on many geographical factors. You
will realize from the activity above that there are
very few such services which are not dependent
on natural factors completely. Climate,
topography, nearness to the sea or continental
location are some of the geographical factors,
which may affect tertiary activities.
The secondary activities are not only
dependent on how long the perishable raw
material will last but also the mode of transport
through which the raw material is to be delivered.
For example, for international export of a
product like grape obtained through agriculture,
using airways will be a better option, while
sending cotton through water transport will be
more profitable.
The human settlements all over the
world have developed as an effect of various
favourable geographical factors. Markets, be
it retail or wholesale, always occur near these
settlements. A secondary activity can occur
away from the settlements but markets will not.
They are always found near the settlements.
Loading and unloading of goods takes
place at ports and dockyards. Try searching the
names of these places with the help of internet.
(For example, Ghodbunder, Kochi Port trust,
Mumbai Port Trust, Delhi International Cargo
Terminal). You will find that these places are
either located near a water transport or airways.
It is clear from the examples above
that tertiary activities are also controlled by
geographical factors. Transportation is also an
example of this. Now, it is being operated by
advanced technology.
Transportation :
Transportation is a service or facility
through which passengers, freight and industrial
products are carried from one place to another.
Transportation plays a very important role in
development of any country. It is one of the basic
tertiary activities. Development of all economic
activities is dependent on transportation system.
Means of transportation are essential
components of transport systems. They are
the means to carry passengers or freight or a
combination of both, from one place to another.
Means of transportation can be grouped
into three broad categories based on the medium
they use : land, water and air. Each mode has its
own requirements and features and is adapted
to serve the specific demands of freight and
passenger traffic. This gives rise to marked
differences in the ways the these means are
deployed and utilized in different parts of the
world.
Various geographical factors govern the
development of transport. Relief, location and
climate are the three major physical factors.
Generally, it is easier to build rails, roads and
pipelines where relief is not rugged. Dense
forests, hilly and mountainous regions affect
construction of long route rails and roads. For
example, in dense forest and arid regions of
Africa and South America, construction of long
distance roads and rails is difficult.
Coastal area locations are favourable for
development of ports and harbours, especially
broken coastlines. Therefore, not all coastal
areas can be good ports.
With development of technology, air
transport is now used more. But still, major
trade happens through ocean routes. Two canals
which changed the course of transport, Suez
Canal and Panama Canal, were constructed to
avoid long ocean routes.
They changed the use
of ocean routes radically. Suez canal connected
Asia with Europe and Africa. Panama Canal
joined Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
For airways to develop, one needs
favourable climate, advanced technology and
plain regions for airports. Constant fog or smogs,
area with high peaks, become an obstacle for
air transportation.
Trade means the voluntary exchange of
goods and services, where two or more parties
are involved. Barter system was an initial form
of trade practised by the primitive societies.
There was only an exchange of goods. Today,
trade occurs in goods and services. Bilateral or
multilateral trades are major types of international
trade. Trades can be carried out within a country
too. Trades can be affected by many factors.
International trade is a result of specialisation in
production and human resources.
International trade occurs when it is
mutually beneficial to trading partners and when
it is a comparative advantage for both, rather
than producing in their own countries. It may
occur to you that this is an economic concept,
then why are we discussing this in geography?
But, actually, the foundation of this activity lies
in geography. You will relate to it when you read
the explanation further
Tertiary Economic Activities Exercise | Class 12 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities
- Maharashtra Board Class 12 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities
- Tertiary Economic Activities Exercise | Class 12 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities
- Chapter 6 Tertiary Economic Activities Geography Class 12 .
- secondary economic activities exercise
- primary economic activities exercise
- navneet geography digest std 12 pdf download
- geography practical class 12 hsc solutions pdf
- primary economic activities class 12 notes
- tertiary activities include both services and exchange
- geography class 12 chapter 6 exercise
- region and regional development exercise
Maharashtra State Board 12th Std Geography Textbook Solutions Digest
| Chapter No | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Population Part 1 |
| Chapter 2 | Population Part 2 |
| Chapter 3 | Human Settlements and Land Use |
| Chapter 4 | Primary Economic Activities |
| Chapter 5 | Secondary Economic Activities |
| Chapter 6 | Tertiary Economic Activities |
| Chapter 7 | Region and Regional Development |
| Chapter 8 | Geography: Nature and Scope |

.webp)